The proposed BLM Public Lands Rule regulation included two citations to papers. I decided to take a look at them and see what helpful info I could glean from them. They are both DOI (USGS) products.
********************
The first one is called “A Sagebrush Conservation Design to Proactively Restore America’s Sagebrush Biome,” with a bunch of authors and prepared in cooperation with WAFWA and the USFWS. I’m assuming it’s a bird-o-centric view. Still, they are talking about ecological integrity.
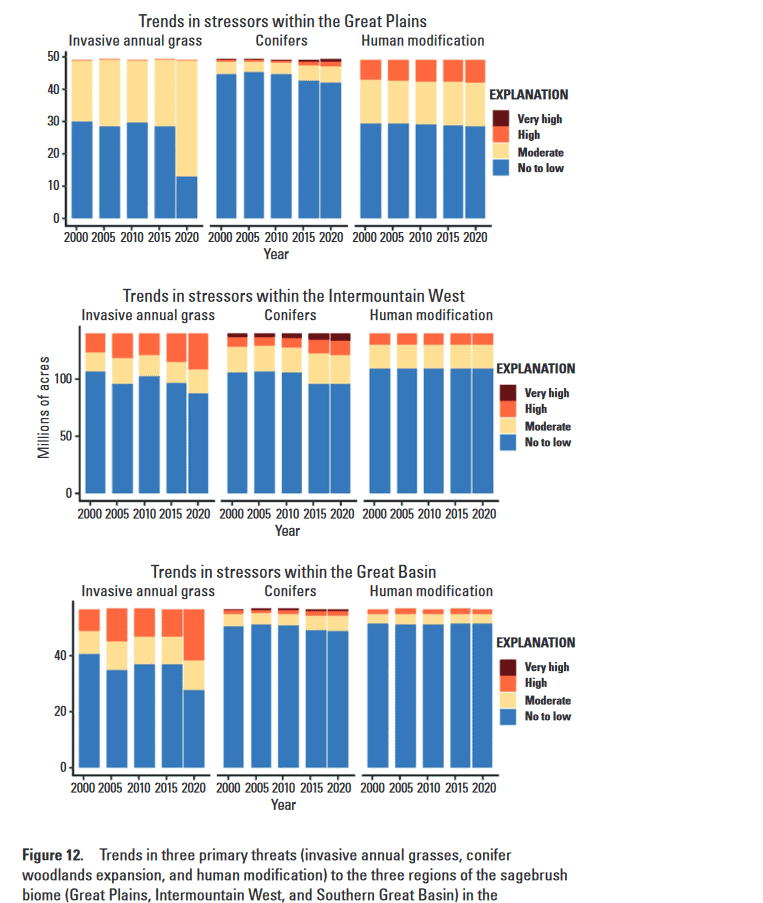
These ongoing and anticipated losses in areas of high ecological integrity have been driven primarily by the incursions of invasive annual grasses across the three ecoregions (fig. 12). By 2020 (the final year examined), more areas were moderately or highly threatened by invasive annual grasses than in any year prior, including more than one-half of the Southern Great Basin region. A sudden increase relative to 2016 (the penultimate year examined) was particularly pronounced in the Great Plains region, although none of this region had been deemed high risk. The threat of conifer expansion into the no to low category showed an increase compared with that of 2001; however, expansion into this category held steady from 2016 to 2020, especially in the Intermountain West and Southern Great Basin regions. The team also documented infill of conifer stands, showing an increase in the areas classified as high or very high risk, especially in the Intermountain West region. The footprint of human modification remained relatively constant over time within regions, but the footprints varied considerably across regions—for example, more than 90 percent of the Southern Great Basin region remained at no to low risk by 2020 compared with only 60 percent of the Great Plains region remaining at this level.
From the summary:
Given the number of threats, the scale at which they operate, and the dispersed authority and responsibility to regulate and address threats, this effort may take an almost unprecedented degree of cooperation and collaboration, a bold vision, and ambitious goal setting. To date, substantial investments in collaborative efforts to remove conifers expanding into sagebrush plant communities by Oregon’s SageCon partnership, the Sage-Grouse Initiative, and the Utah Watershed Restoration Initiative have matched the rate of loss to conifer expansion within the Great Basin (Reinhardt and others, 2020).
The results in this study indicate that a similar focus could allocate limited conservation resources to where and when they have the highest probability of achieving desired uplift, which the design can inform.
**********************************
From this paper, a person could develop a regulation that would
- Encourage collaborative work with other agencies and local collaboratives to reduce impacts. States and Tribes are important partners, involved in the development of any regulation (not at the comment period).
2. Since invasives are a big problem, drawing a line around an area and keeping people out is unlikely to move towards ecological integrity. Same with those pesky conifers.
3. Invasives also change wildfire frequency, and different grazing techniques can be used to reduce fire danger.
It’s hard for me to see that mapping “intactness” which doesn’t take into account the threat of invasives, determining what is “land health” for other activities, or conservation leasing will help with any of these problems. On the other hand, if you want to keep people out and let whatever happen, that’s fine too, but it’s not promoting biodiversity, natural range of variation nor probably carbon.
************************

(David Swanson/
AFP via Getty Images)
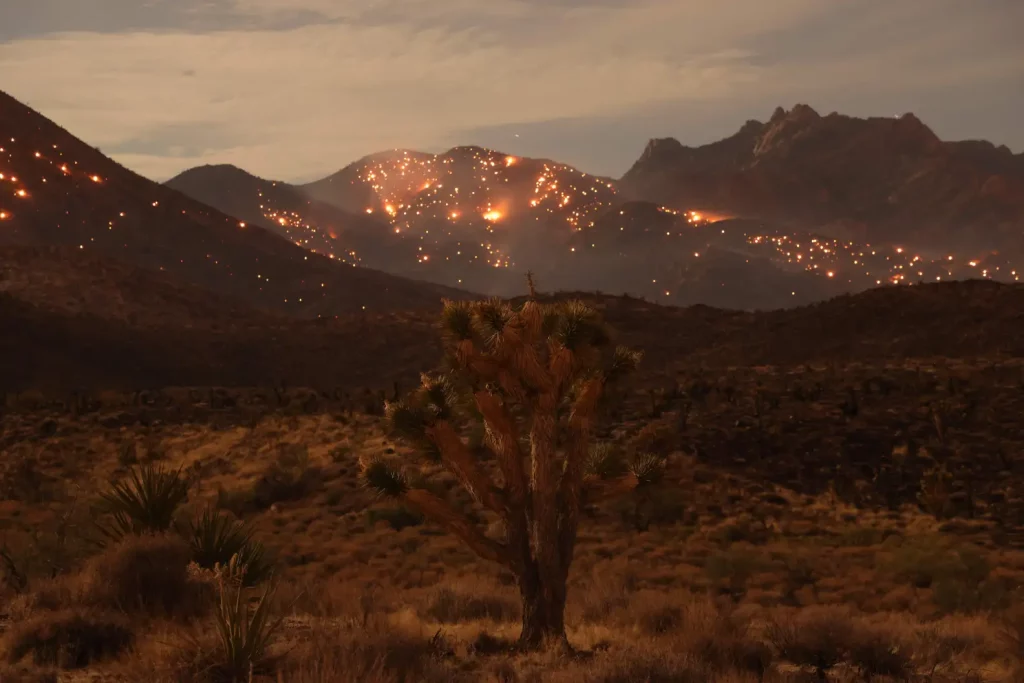
We’ve seen a bit of this with the current fire in the Mojave National Preserve, burning up Joshua Trees.
Interesting story on a fire in the Mojave National Preserve and the Joshua Trees from the LAist.
More than 77,000 acres of desert landscape have burned over the past few days in the York Fire, the largest on record for the Mojave National Preserve, as high temperatures and strong winds drove flames across the border into Nevada on Sunday.
Flames up to 20 feet tall have been spotted as the fire has torn through mixed desert scrub, yucca, pinyon juniper, and invasive plants like red brome, all of which saw a lot of growth during the recent wet winter.
“I was just driving through that area a week or two before the York Fire and thought ‘This place is going to burn.’ There’s just fuel everywhere,” said Debra Hughson, deputy superintendent of the preserve.
Fires like this have long been rare in Mojave desert ecosystems, with some estimates putting the fire return interval at every couple hundred years. Now, they’re becoming a feature of the landscape, increasing in frequency and jeopardizing the recovery of native species, including Joshua trees. Just a few years ago, the nearby Dome Fire burned more than 40,000 acres and destroyed more than 1 million of the famous trees.
“Fires this big are really a game changer in the desert,” said Todd Esque, research ecologist with the U.S. Geological Survey.
The role invasive species are playing
Invasive species including red brome, cheatgrass and Sahara mustard are helping drive the new fire regime. The weeds thrive in the desert environment, filling in the space between Joshua trees, carrying the fire from one tree to the next. And after fire clears things out, the invasive species quickly move back in.
“They burn every 10 years, which happens in some places where there’s Joshua trees now, because of weeds…now it’s just a straw-colored two dimensional landscape of rolling hills,” Esque said.
A pullback on grazing in this area of the Mojave has led to an increase in the growth of native vegetation as well, with grasses like big galleta also carrying fire.
Joshua trees aren’t really all that adapted to withstand fire. They can re-sprout from their roots after burning, but that’s not always the case if the fire’s too intense.
Even if they do pop back up, their growth rate of roughly three centimeters per year is quite slow, meaning the landscapes we’ve long grown fond of are likely not coming back, at least in our lifetimes. They could take more than a century to repopulate — assuming they do at all. That’s because hotter temperatures and longer droughts, punctuated by frequent fires in the era of climate change, make regrowth more difficult.
The fire is also burning through critical habitat for the desert tortoise, which is listed as a threatened species.
You don’t think people have something to do with how invasive species spread?
https://www.pbs.org/newshour/science/hikers-can-take-these-simple-steps-to-help-reduce-the-spread-of-invasive-plant-species
You can’t say controlling access (horses and vehicles maybe more so) wouldn’t help.
And the whole point of conservation leasing is, “conservation leases would be a tool available to entities seeking to restore public lands or provide mitigation for a particular action.” A big part of restoration promoted by the BLM rule would surely be about invasive species.
chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.blm.gov/sites/default/files/docs/2023-05/Conservation%20Leasing%20fact%20sheet%205-11-23.pdf
Of course I do! That’s why there are regulations and education programs for hay, boat, firewood and so on.
And I think we’re back to partners have done restoration treatments without conservation leasing.. so why is it needed?.